OK,
Got this request from management.
CISSP.
Not really a useful cert, it is all theory and no hands on.
So it should last for a while and is a good basic to have.
The Exam has ten domains.
You can go online to
https://www.isc2.org/cissp-domains/default.aspx
and download the CISSP domains, you just have to fill in some details.
there are three books you can use.
1. Shon Harris CISSP all in one 6th edition.
2. Official ISC2 guide to CISSP
3. CISSP: Certified Information Systems Security Professional Study Guide James
4. CISSP study guide by Eric and some other people.
The rest seem to be duds based on the amazon reviews.
Let's do it.
I'll start with the CISSP by James Stewart.
I'll start with the CISSP by James Stewart.
Chapter 1
The first domain here is ACCESS CONTROL
What is Access control.
Any measure you put in place, the measure can be hardware, software or a managerial policy.
Any measure you put in place, the measure can be hardware, software or a managerial policy.
That measure identifies the user, determines if he is authorized, grants or restricts, then logs this.
SUBJECT - active entity
OBJECT - passive entity.
A subject will use an object
A user will access a file
A process will write to a file
A USER {subject} will access an object.
The OWNER is the owner of the object and determines the use of it.
A CUSTODIAN takes care of the object for the owner and makes it available for the users.
The goal of the security it to provide the CIA of IAC
Confidentiality - that it has not been read
Confidentiality - that it has not been read
Integrity - that it has not been changed.
Availability - that it is available online
Policies
A security policy is made by Senior leadership and is used as the guiding IDEA of security that is needed.
It states rough goals and ideas, it does not state how to achieve this.
It states rough goals and ideas, it does not state how to achieve this.
User rights to do something applies to a user
The file permissions applies to an object
Privilege is the combination of both
Access control types
Prevent - something from happening fence
Detect - it when it happens smoke alarm
Correct - it fix it put out the fire
- Deterrent - scare someone place a big shiny light to scare thieves
- Recovery - replace the burnt servers
- Directive - use a Direction like a sign
- compensation - looks to compensate for a problem
- Administrative control - hiring practices
- Logical controls - software + Hardware like passwords
- physical control - Fence, wall, door
The Goal is to layer the above in circles or layers.
Physical to stop you going in,
logical in case you got in you can't use it
Administrative like requiring a manager to type in his password to get cash out.
Access control security elements
Identify the user - username or name
Authenticate the user - ID or a password
Authorize - check to see if he is allowed in or use Access lists.
Accountability - Write his name down, so you know he came in or in IT log it in the syslog or audit log.
Authentication has 3 types
Type 1 - what you know like a password
Type 2 - what you have like a security HID card
Type 3 - something you are like your finger print.
Two factor authentication will use two of the above.
*** you can also use somewhere you are, for example dial back or the pc location [type2]
Type 1 password
Weak, users re-use the password and it can be guessed.
Users sometimes write them down if they are complex.
They can be hacked using brute force or other attacks.
They can be hacked using brute force or other attacks.
They usually use a HASH to compare the passwords so they don't send them on the network.
Selection -
length - the longer they are the more difficult to crack with a brute force
complexity- the more complex the more difficult
history - prevents users from re-using their passwords.
To avoid dictionary - don't use words
to avoid brute - use numbers and capitalization
to avoid guessing - don't use personal details.
Passphrase - I@mstudying4CISSP =Easier to remember. Increases the length to counter brute.
Cognitive password -Number of questions like 1.dog name 2. mother maiden -used for password recover
Type 2 - what you have
Smartcard -- static token
CAC common access card
PIV personal identification verification
PIV personal identification verification
Token - generates a password.
Token synchronous - both the token and the server must be time synchronized
Token Asynchronous - the server will send a challenge, you type the challenge in and get a password.
Type 3 - what you are.
A photo on an ID - you are the photo.
Fingerprint
Face shape scan
Retina can show diabetes or sick
IRIS - color area
Hand geometry
Voice pattern recognition
Signature or keyboard typing dynamics
Errors on this are - Type 1 error false negative FRR false rejection - it does not recognize me.
Errors on this are - Type 2 error false positive FAR acceptance rate - it allowed the thief in .
CER crossover rate is when you change the sensitivity of the device and they match.
Low CER is more accurate.
Low CER is more accurate.
A false rejection is considered much more preferable. That way the admin can double check the identity.
registration is done using enrollment - your enroll, fill the paper work, get a measurement and the DB will
register you and create a record or a reference profile
register you and create a record or a reference profile
Access control techniques
Need to know -An example is, if you are not serving in Iraq you don't need to see that regions top secret
even if you have a top secret clearance.
even if you have a top secret clearance.
Least privilege - gives you the minimum permissions so you can do your job.
Separation of duty - split the task so that two people or more are required for it.
Discretionary access control - DAC =
The owner of the object can define the access level of the subjects to it.
Each object has an ACL
Non-discretionary.
This is centrally controlled.
Rule - based access control an example is a firewall. It has rules and the owners get no say.
Role Based Access Control - RBAC, the explanations in the book are shit so let's do it this way.
Let's say we make a role - new_client_creator.
The role can create a new client.
The actions are open a a folder for them permission + add a line in the DB + change the address lines
The role can create a new client.
The actions are open a a folder for them permission + add a line in the DB + change the address lines
Now, instead of you having permissions to each item with your user. We give those permissions to that
role and we assign you that role.
role and we assign you that role.
So in RBAC you package the role to equate a work task and then you assign the work task/role
just to make sure.
This is not you assigning accounting group to the accountant.
You need to create a work task, called add_new_provider and assign him a task
This is not you assigning accounting group to the accountant.
You need to create a work task, called add_new_provider and assign him a task
Thanks to Greg Shields for doing a better job than the rest of the authors.
MAC mandatory access control - {tip they have labels}
The first question to ask is
What is your security level - you can access items at your current security level and lower.
The second question is
Do you need to know this to do your job
So in real life.
Let's say I work in Iraq and I do security for oil shipments.
Let's say I work in Iraq and I do security for oil shipments.
My role is shipping oil
So the oil trucks will be marked need to know- shipping oil secret
So the oil trucks will be marked need to know- shipping oil secret
The route maps in Iraq will be marked need to know shipping oil secret
The oil dollar value in iraq will be marked need to know shipping oil top secret
The list of Iraqi collaborators will be marked TOP secret but the need to know will be CIA
The route maps in Afghanistan will be marked need to know Afghanistan
So let's see.
I have top secret but I can't see what routes they use in Afghanistan as it is not my theater of operations.
I have top secret but I can't see what routes they use in Afghanistan as it is not my theater of operations.
I can't see the list of Iraqi collaborators because I don't have a need to know, it is not relevant to my role
even though I have administrator account or as we call it here top secret.
even though I have administrator account or as we call it here top secret.
So as you can see I can do my job.
I can see the oil trucks.
I can see the routes
I can see the oil trucks.
I can see the routes
and I can make accounting dollar cost oil reports.
Now if I have a subordinate I can give him secret,
and then he can only
and then he can only
see oil trucks
see truck routes
so he can just do his job which would be to ship the trucks around Iraq.
So hierarchical MAC uses only the secret and top secret
compartmentalized MAC uses compartments only like CIA/shipping oil/ Afghanistan
Hybrid is a mix of the two
centralized access control - means one administrator location kind of like a dictator.
Distributed access control - means you let every "location" or dept be in charge kind of the states in the USA making their own laws.
Single sign on-
This is like the USA passport, it works in all the states and countries.
This is like the USA passport, it works in all the states and countries.
Kerberos.
Uses a KDC Key distribution center - This is the Ministry of Interior it gives you a key or passport.TGT
Uses a KDC Key distribution center - This is the Ministry of Interior it gives you a key or passport.TGT
we can call this passport TGT ticket granting ticket.
Now when i want to access a resource, I present my TGT to the LDAP server or security guard
and he let's me have access to the resource.
In kerberos the timing must be synchronized to within 5 minute difference for it to work.
Federated Identity.
Another way to move identity credentials between separate security domains.
For example you give your ID card to the university so you can access their systems is to use
Another way to move identity credentials between separate security domains.
For example you give your ID card to the university so you can access their systems is to use
an intermediary .
XML has tags <user> Saar </user> <password> test123 </password>
SAML security Assertion Markup Language uses XML for SSO.
SPML service provision markup uses DSML
DSML takes LDAP and uses XML to represent this.
Extensible Access Control Markup Language (XACML) used for federated Role Base.
Other
You can use manual scripts, when you log in. The system will log you in to other systems too.
RADIUS - dial in user, this was based on autheticating dial up users. The user connects to a device.
The device will forward the request to the Radius server.
Radius can provide AAA,
authentication and authorization at the same time of the user
Accounting of all of this.
Tacacs - is old UDP49
xtacacs - was made by Cisco only UDP49
Tacacs+ is open, the key here is it encrypts all of the authentication information. TCP49
It also logs all the commands and checks them against your authorization.
So better for an administrator.
Diameter
Supports more products.
TCP 3868 or SCTP 3868
more reliable and uses IPSEC and TLS.
Mechanisms.
Implicit deny on all items unless it is allowed - usually a firewall has this at the end deny all
ACL - an ACL is applied on each object
Capability table- this is a different view it is applied on the subject.
ACL
Capability table.
Constrained view.
So, I can remove the RUN button.
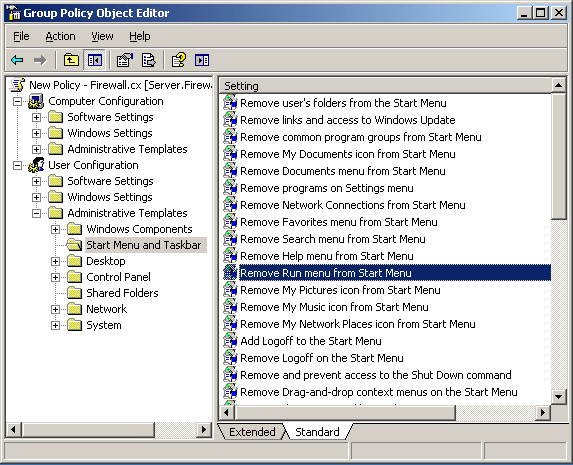
So I have constrained the users view and he CAN"T see the the RUN.
It is still there if you know how to get to it, but he can't see it in the start menu.
Content view - means I limit the number of fields you can see but the admin can see the whole table. This is similar to a view.
Context-view In this case you use a context, for example the time of day.
So from 12-6 am in the morning, when you log in to the corporate web, you can't do any work actions
only read.
Identity and access lifecycle
Provision the user - Hire, make him sign agreements, add him to groups etc.
Review - every so often review the account, make sure he did not get more permissions than he needs. In IT we used to have a script that would remove all 'local" administrators on windows and replace
them with the group called "helpdesk administrators" this helped return PCs back to normal.
Revocation - when someone leaves, you need to disable and remove the account.
As a best practice, this should be immediate.....
Provision
review
revoke
PRR!!!!

Chapter 2
Access control Attacks and how to monitor this.
One of the goals of the Access Control is to prevent unauthorized access to objects
Disclosure = C
Alteration = I
Availability = A
Crackers = malicious intent
Hacker = non malicious intent
attacker = someone who wants to exploit the vulnerability
RISK is the likelihood that a Threat Agent --> Threat --> takes advantage of a vulnerability --> of an asset.
Asset valuation.
Risk management is the service of providing that risk evaluation.
Server can be $20000 in hardware but if you are an ecommerce it can generate
that much every day. So losing the server to fire would cost you.
7 days * $20000 = $140,000 in losses + the server hardware.
The above also helps in evaluating whether the cost of the countermeasure is worth
the investment.
Threat Modeling
Each of these assets can be attacked.
The attacks are also called threats
The threats can be done by attackers or threat agents
or they can be done by natural disaster, user fault etc.
Your goal is to reduce the number of threats
and reduce the severity of the threats.
You can look at it from the
Threat agent - this is the hacker in Russia, what can he reach.
or the asset view - ie this is my asset and this is the attacks that can be done on it
Software view - if you are developing software.
APT - advanced persistent threat : group of hackers targeting your network.
Vulnerability
The potential of the threat to exploit a weakness.
Vulnerability scans are a full time job for some companies.
Attacks
Access aggregation.
Collect many pieces of non-sensitive info to build a picture.
Password attacks - hack the administrator password, since very few organizations change it also it won't get disabled even after repeated failures.
to counter that, you turn on logging and alerts, Microsoft also recommends you rename it so it is not so obvious. you can leave the "administrator" as a honey pot.
If two separate passwords create the same hash that is called a collision.
The birthday attack focuses on collisions. There is a high chance of collisions.
If you have a word that makes the same hash it is as good as the original password.
So let's go back and explain the hacking.
In the good old days PAP would send your password in clear text.
If you use a Sniffer, you capture the traffic on the wires and find out the password .
So they came up with verifying your password by sending a hash back and forth and not the original
password.
So when you try to guess a password like.
On my XP, I will type password2013.
The XP will create a HASH and send over the HASH.
The Server that is authenticating you will compare your HASH to his HASH(server)
If they match he will assume the password is correct.
So as we explained, a collision is when another word creates the same HASH.
In this case the server can't tell the difference and let's you in.
Now, if your password is a word or even an upped-word which is a word + 1 number.
A dictionary attack can easily figure it out. This is because there are only 500,000 words.
I'd guess this is the equivalent of 6 letter password. So it would be pretty quick to decipher.
Now, if you have made it too short and not very complex eventually a brute force attack will get it.
Now, if they have an offline copy of the DB like a SAM file that stores the windows passwords
from a laptop HD they stole, it would be quicker as they can run more runs per second.
Some people, create a rainbow table that has a long list of passwords that have already had their hash calculated. So this saves you the CPU cycles of each plaintext to hash conversion.
rainbow tables usually go for the more predictable items.
To protect against the Rainbow table you add a hash, now the rainbow table needs to be recalculated against the hash and you can also salt each password which renders the table useless.
Spoofing
Spoof the Email
Spoof the phone number.
Social engineering
Simply asking the user for his password while pretending to be someone in the organization.
Phishing
Getting you to click on links.
Spear phishing
Targeting specific people
Whale phishing
targeting people high up.
Vishing
is Phishing using VOIP to get details.
Smart card attack, or side-channel
You listen in proximity, when the card sends an RF you copy it.
DOS or DDos allow you to attack the availability.
Prevention
Control access to the systems that way they can't get an offline copy, put keyloggers etc
Control electronic access to the password file
encrypt the password files
Strong passwords
mask passwords **** to prevent over the back snoopers.
Use multifactor authentication
use lockout mechanism
user alerts
Use last logon notification so the user can tell if there have been any other attempts.
Educate the users on passwords and security
Audit the access
Scan for vulnerabilities by yourself and not wait - ie be proactive.
Use logs
protect the logs
monitor and analyze the data from the files. SIEM security information event management
Use Audit trails and let users know about them.
clipping level also called a threshold, don't let me know about 1 failed attempt only if 3 happen.
Keystroke monitoring- can be used by management
Traffic analysis - analyze the traffic and the patterns IPS
network data loss prevent - scan for key words or SS social security numbers going out.
Audit
the Access
the process
entitlements of users to prevent growth of privileges or creeping.
or you can also use external audits.
This one is nice, Dual administrator.
So one account is SaarHarel the other one is networkadmin that way when I go surfing to bad sites, I use the regular one and when I do maintenance I use the "networkadmin" one.
Protect the results of audits, so they can't be used to target you.
RADIUS - dial in user, this was based on autheticating dial up users. The user connects to a device.
The device will forward the request to the Radius server.
Radius can provide AAA,
authentication and authorization at the same time of the user
Accounting of all of this.
Tacacs - is old UDP49
xtacacs - was made by Cisco only UDP49
Tacacs+ is open, the key here is it encrypts all of the authentication information. TCP49
It also logs all the commands and checks them against your authorization.
So better for an administrator.
Diameter
Supports more products.
TCP 3868 or SCTP 3868
more reliable and uses IPSEC and TLS.
Mechanisms.
Implicit deny on all items unless it is allowed - usually a firewall has this at the end deny all
ACL - an ACL is applied on each object
Capability table- this is a different view it is applied on the subject.
ACL
Capability table.
Constrained view.
So, I can remove the RUN button.

So I have constrained the users view and he CAN"T see the the RUN.
It is still there if you know how to get to it, but he can't see it in the start menu.
Content view - means I limit the number of fields you can see but the admin can see the whole table. This is similar to a view.
Context-view In this case you use a context, for example the time of day.
So from 12-6 am in the morning, when you log in to the corporate web, you can't do any work actions
only read.
Identity and access lifecycle
Provision the user - Hire, make him sign agreements, add him to groups etc.
Review - every so often review the account, make sure he did not get more permissions than he needs. In IT we used to have a script that would remove all 'local" administrators on windows and replace
them with the group called "helpdesk administrators" this helped return PCs back to normal.
Revocation - when someone leaves, you need to disable and remove the account.
As a best practice, this should be immediate.....
Provision
review
revoke
PRR!!!!

Chapter 2
Access control Attacks and how to monitor this.
One of the goals of the Access Control is to prevent unauthorized access to objects
Disclosure = C
Alteration = I
Availability = A
Crackers = malicious intent
Hacker = non malicious intent
attacker = someone who wants to exploit the vulnerability
RISK is the likelihood that a Threat Agent --> Threat --> takes advantage of a vulnerability --> of an asset.
Asset valuation.
Risk management is the service of providing that risk evaluation.
Server can be $20000 in hardware but if you are an ecommerce it can generate
that much every day. So losing the server to fire would cost you.
7 days * $20000 = $140,000 in losses + the server hardware.
The above also helps in evaluating whether the cost of the countermeasure is worth
the investment.
Threat Modeling
Each of these assets can be attacked.
The attacks are also called threats
The threats can be done by attackers or threat agents
or they can be done by natural disaster, user fault etc.
Your goal is to reduce the number of threats
and reduce the severity of the threats.
You can look at it from the
Threat agent - this is the hacker in Russia, what can he reach.
or the asset view - ie this is my asset and this is the attacks that can be done on it
Software view - if you are developing software.
APT - advanced persistent threat : group of hackers targeting your network.
Vulnerability
The potential of the threat to exploit a weakness.
Vulnerability scans are a full time job for some companies.
Attacks
Access aggregation.
Collect many pieces of non-sensitive info to build a picture.
Password attacks - hack the administrator password, since very few organizations change it also it won't get disabled even after repeated failures.
to counter that, you turn on logging and alerts, Microsoft also recommends you rename it so it is not so obvious. you can leave the "administrator" as a honey pot.
If two separate passwords create the same hash that is called a collision.
The birthday attack focuses on collisions. There is a high chance of collisions.
If you have a word that makes the same hash it is as good as the original password.
So let's go back and explain the hacking.
In the good old days PAP would send your password in clear text.
If you use a Sniffer, you capture the traffic on the wires and find out the password .
So they came up with verifying your password by sending a hash back and forth and not the original
password.
So when you try to guess a password like.
On my XP, I will type password2013.
The XP will create a HASH and send over the HASH.
The Server that is authenticating you will compare your HASH to his HASH(server)
If they match he will assume the password is correct.
So as we explained, a collision is when another word creates the same HASH.
In this case the server can't tell the difference and let's you in.
Now, if your password is a word or even an upped-word which is a word + 1 number.
A dictionary attack can easily figure it out. This is because there are only 500,000 words.
I'd guess this is the equivalent of 6 letter password. So it would be pretty quick to decipher.
Now, if you have made it too short and not very complex eventually a brute force attack will get it.
Now, if they have an offline copy of the DB like a SAM file that stores the windows passwords
from a laptop HD they stole, it would be quicker as they can run more runs per second.
Some people, create a rainbow table that has a long list of passwords that have already had their hash calculated. So this saves you the CPU cycles of each plaintext to hash conversion.
rainbow tables usually go for the more predictable items.
To protect against the Rainbow table you add a hash, now the rainbow table needs to be recalculated against the hash and you can also salt each password which renders the table useless.
Spoofing
Spoof the Email
Spoof the phone number.
Social engineering
Simply asking the user for his password while pretending to be someone in the organization.
Phishing
Getting you to click on links.
Spear phishing
Targeting specific people
Whale phishing
targeting people high up.
Vishing
is Phishing using VOIP to get details.
Smart card attack, or side-channel
You listen in proximity, when the card sends an RF you copy it.
DOS or DDos allow you to attack the availability.
Prevention
Control access to the systems that way they can't get an offline copy, put keyloggers etc
Control electronic access to the password file
encrypt the password files
Strong passwords
mask passwords **** to prevent over the back snoopers.
Use multifactor authentication
use lockout mechanism
user alerts
Use last logon notification so the user can tell if there have been any other attempts.
Educate the users on passwords and security
Audit the access
Scan for vulnerabilities by yourself and not wait - ie be proactive.
Use logs
protect the logs
monitor and analyze the data from the files. SIEM security information event management
Use Audit trails and let users know about them.
clipping level also called a threshold, don't let me know about 1 failed attempt only if 3 happen.
Keystroke monitoring- can be used by management
Traffic analysis - analyze the traffic and the patterns IPS
network data loss prevent - scan for key words or SS social security numbers going out.
Audit
the Access
the process
entitlements of users to prevent growth of privileges or creeping.
or you can also use external audits.
This one is nice, Dual administrator.
So one account is SaarHarel the other one is networkadmin that way when I go surfing to bad sites, I use the regular one and when I do maintenance I use the "networkadmin" one.
Protect the results of audits, so they can't be used to target you.





